فهرست مطالب
Biolmpacts
Volume:8 Issue: 2, Jun 2018
- تاریخ انتشار: 1397/03/30
- تعداد عناوین: 8
-
-
Pages 77-79Layer-by-layer fabrication of three dimensional (3D) objects from digital models is called 3D printing. This technology established just about three decades ago at the confluence of materials science, chemistry, robotics, and optics researches to ease the fabrication of UV-cured resin prototypes. The 3D technology was rapidly considered as a standard instrument in the aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods production factories. Nowadays, research interests in the 3D printed products have been raised and achieved ever-increasing traction in the pharmaceutical industry; so that, the first 3D printed drug product was approved by FDA in August 2015. This editorial summarizes the competitive advantages of the 3D printing for the made-on-demand, personalized and complex products, manufacturing of which establish opportunities for enhancing the accessibility, effectiveness, and safety of drugs.Keywords: 3D printing, Layer, by, layer fabrication, Made, on, demand drugs, Personalized medicines
-
Pages 81-89IntroductionIn the recent years, green synthesis is a novel method without some disadvantages of physical and chemical methods. In this approach, bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, and plants may be applied without utilizing toxic and expensive materials for metal nanoparticles (MNPs) preparation.MethodsIn this study, we used Taguchi method to obtain optimum conditions in titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticle (NPs) biosynthesis by Halomonas elongata IBRC-M 10214. Design and analysis of Taguchi experiments (an orthogonal assay and analysis of variance [ANOVA]) carried out by the Qualitek-4 software. Effects of TiO(OH)2, incubation temperature, and culturing time for synthesis of TiO2 NPs as well as ZnCl2 concentration, glucose concentration, and incubation temperature for preperation of ZnO NPs were evaluated as the controllable factors with 3 levels. Characterization of TiO2 and ZnO NPs were determined by UV-Vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis. Also, the antimicrobial properties of these NPs were investigated based on agar diffusion assay of NPs dispersed in batch cultures using Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 43300 as multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria.ResultsIt was evaluated that TiO2 and ZnO NPs had respectively average diameter sizes of 104.63±27.75 and 18.11±8.93 nm with spherical shapes. In contrast to the TiO2 NPs without antibacterial activity, the ZnO NPs had antibacterial effects at 0.1 and 0.01 M of (ZnCl2).ConclusionThe ZnO NPs have the antibacterial effect that can be operative in the medicinal aspect for fighting against prominent MDR bacteria such as E. coli ATCC 25922 and S. aureus ATCC 43300. In total, this study presents simple method in biosynthesis of TiO2 and ZnO NPs with low expense, eco-friendly, and high productivity properties.Keywords: Antibacterial activities, Biosynthesis, Halomonas elongata IBRC, M 10214, Metal nanoparticles, Optimization, Taguchi method
-
Pages 91-98IntroductionStarch-based materials were designed using a special extrusion die in order to obtain a tube-shaped device for application to salivary duct treatment in the field of endoscopy, i.e., sialendoscopy.MethodsExtrusion process was used to produce starch tubes. Mechanical properties of the dry tube before implantation were determined using an axial compression test. A finite element study was carried out to simulate the behavior of the hydrated tube under external axial pressure. Hydrolysis of these devices in a simulated salivary solution was studied, as well as its glycerol kinetics release. An animal short-term implantation model for salivary ducts was proposed as a feasibility study for starch tube-shaped devices.ResultsA continuous production of regular and size-controlled tubes was obtained. The very small diameter obtained, less than 2 mm, corresponds to the requirement of being insertable in a human salivary duct by using sialendoscopy guidewire. Finite element analysis showed that the starch tube can still support an external pressure higher than 0.2 MPa without irreversible damage. After 4 days of implantation, the host response is encouraging and the inflammatory response for this type of procedure remains normal.ConclusionThese devices were adapted to sialendoscopic guidewires and able to be implanted in the salivary ducts of pigs. If a longer lasting tube is required, the crystallinity of the starch material should be improved.Keywords: Extrusion, Degradable device, Sialendoscopy, Starch, Tube
-
Pages 99-106IntroductionIn the recent decades, starch has been modified using different methods for the various forms of applications. Some new starch derivatives were prepared through a simple and convenient method in the grafting of amino acids: L-alanine, L-leucine and L-phenyl alanine to starch.MethodsFirst, the amine groups of amino acids were protected using phthalic anhydride then the acidic side of amino acids were activated with chlorination using thionyl chloride, and the resultant acid chlorides were reacted with starch in aqueous media at room temperature.ResultsPerforming the various spectroscopy experiments on the obtained compounds showed that the new derivative of starch has been formed. The structure of all synthesized materials was determined and confirmed using common spectroscopy methods and their thermal behavior was examined using DSC experiment.ConclusionNew amino acid derivatives of starch and their nanocarriers successfully prepared through a simple and convenient method. The size of nanocarriers evaluated using DLS and TEM experiments. The spherical shape of particles shows that nanocarriers have been formed and the size of these particles are approximately 92, 137 and 97 nm. Performing the wettability test determined that all the resulted materials are soluble in water. Nanocarriers of the obtained modified starches were prepared using dialysis method and naproxen was utilized as a model drug molecule. The drug release dynamics in buffered solution were studied and investigation of the drug release mechanism showed that in case of L-alanine- and L-phenylalanine-modified starches, drug release followed the Fickian diffusion with a slight deviation.Keywords: Amino acid, Drug delivery, Starch, Nanocarrier
-
Pages 107-116IntroductionThere is a fundamental need to characterize multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) toxicity to guarantee their safe application. Functionalized MWCNTs have recently attracted special interest in order to enhance biocompatibility. The aim of the current work was to study the underlying toxicity mechanism of the -OH-functionalized MWCNTs (MWCNTs-OH), using the powerful NMR-based metabonomics technique.MethodsFollowing intraperitoneal single-injection of mice with 3 doses of MWCNTs-OH and one control, samples were collected at four time points during 22-days for NMR, biochemistry, and histopathology analysis. Metabolome profiling and pathway analysis were implemented by chemometrics tools and metabolome databases.ResultsBased on the 1H-NMR data, metabolic perturbation induced by MWCNTs-OH were characterized by altered levels of steroid hormones, including elevated androgens, estrogens, corticosterone, and aldosterone. Moreover, increased L-lysine, aminoadipate, taurine and taurocholic acid and decreased biotin were observed in the high-dose group (1 mg.kg-1 B.W.) compared to the control. The findings also indicated that steroid hormone biosynthesis, lysine biosynthesis, and biotin metabolism are the most affected pathways by MWCNTs-OH.ConclusionThese pathways can reflect perturbation of energy, amino acids, and fat metabolism, as well as oxidative stress. The data obtained by biochemistry, metabonomics, and histopathology were in good agreement, proving that MWCNTs-OH was excreted within 24 h, through the biliary pathway.Keywords: Chemometrics, Metabolomics, Multi, walled carbon nanotubes, NMR, Toxicity
-
Pages 117-127IntroductionSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) can be functionalized with various agents (e.g., targeting and therapeutic agents) and used for targeted imaging/therapy of cancer. In the present study, we engineered doxorubicin (DOX)-conjugated anti-mucin-1 (MUC-1) aptamer (Ap)-armed PEGylated SPIONs for targeted delivery of DOX molecules to the breast cancer MCF-7 cells.MethodsThe SPIONs were synthesized using the thermal decomposition method and modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG) to maximize their biocompatibility and minimize any undesired cytotoxicity effects. Subsequently, DOX molecules were loaded onto the SPIONs, which were further armed with amine-modified MUC-1 aptamer by EDC/NHS chemistry.ResultsThe morphologic and size analyses of nanoparticles (NPs) by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) revealed spherical and monodisperse MNPs with a size range of 5-64 nm. The FT-IR spectrophotometry and 1HNMR analysis confirmed the surface modification of NPs. The cytotoxicity assay of the aptamer-armed MNPs exhibited a higher death rate in the MUC-1 over-expressing MCF-7 cells as compared to the MUC-1 under-expressing MDA-MB-231 cells. The flow cytometry analysis of the engineered Ap-armed SPIONs revealed a higher uptake as compared to the SPIONs alone.ConclusionBased on our findings, the anti-MUC-1 Ap-armed PEGylated SPIONs loaded with DOX molecules could serve as an effective multifunctional theranostics for simultaneous detection and eradication of MUC-1-positive breast cancer cells.Keywords: Breast cancer, Mucin, 1 aptamer, Nanomedicine, SPION, Targeted drug delivery, Theranostics
-
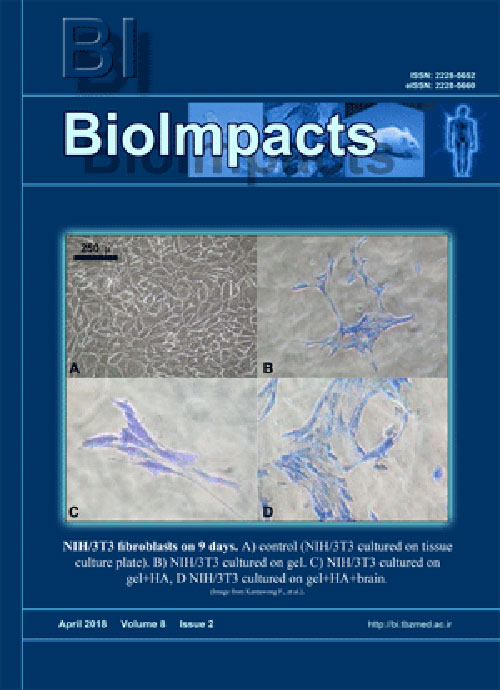
Pages 129-138IntroductionInduced neural stem cells (iNSCs) have the ability of differentiation into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. iNSCs are very useful in terms of research and treatment. The present study offers an idea that biomaterials could be one of the tools that could modulate reprogramming process in the fibroblasts.MethodsGelatin biomaterials were fabricated into 3 types, including (i) gelatin, (ii) gelatin with 1 mg/mL hydroxyapatite, and (iii) gelatin with hydroxyapatite and pig brain. NIH/3T3 fibroblasts were cultured on each type of biomaterial for 7, 9 and 14 days. RT-PCR was performed to investigate the gene expression of the fibroblasts on biomaterials compared to the fibroblasts on tissue culture plates. PI3K/Akt signaling was performed by flow cytometry after 24 hours seeding on the biomaterials. The biomaterials were also tested with the human APCs and PDL cells.ResultsThe fibroblasts exhibited changes in the expression of the reprogramming factor; Klf4 and the neural transcription factors; NFIa, NFIb and Ptbp1 after 9 days culture. The cultivation of fibroblasts on the biomaterials for 7 days showed a higher expression of the transcription factor SOX9. The expression of epigenetic genes; Kat2a and HDAC3 were changed upon the cultivation on the biomaterials for 9 days. The fibroblasts cultured on the biomaterials showed an activation of PI3K/Akt signaling. The human APCs and human PDL cells developed mineralization process on biomaterialsConclusionChanges in the expression of Klf4, NFIa, NFIb, Ptbp1 and SOX9 indicated that fibroblasts were differentiated into an astrocytic lineage. It is possible that the well-designed biomaterials could work as powerful tools in the reprogramming process of fibroblasts into iNSCs.Keywords: Fibroblasts, Induced neuronal stem cells, Cell reprogramming
-
Pages 139-151IntroductionHuman immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a debilitating challenge and concern worldwide. Accessibility to highly active antiretroviral drugs is little or none for developing countries. Production of cost-effective microbicides to prevent the infection with HIV is a requirement. Cyanovirin-N (CVN) is known as a promising cyanobacterial lectin, capable of inhibiting the HIV cell entry in a highly specific manner.MethodsThis review article presents an overview of attempts conducted on different expression systems for the recombinant production of CVN. We have also assessed the potential of the final recombinant product, as an effective anti-HIV microbicide, comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems.ResultsArtificial production of CVN is a challenging task because the desirable anti-HIV activity (CVN-gp120 interaction) depends on the correct formation of disulfide bonds during recombinant production. Thus, inexpensive and functional production of rCVN requires an effective expression system which must be found among the bacteria, yeast, and transgenic plants, for the subsequent satisfying medical application. Moreover, the strong anti-HIV potential of CVN in trace concentrations (micromolar to picomolar) was reported for the in vitro and in vivo tests.ConclusionTo produce pharmaceutically effective CVN, we first need to identify the best expression system, with Escherichia coli, Pichia pastoris, Lactic acid bacteria and transgenic plants being possible candidates. For this reason, heterologous production of this valuable protein is a serious challenge. Since different obstacles influence clinical trials on microbicides in the field of HIV prevention, these items should be considered for evaluating the CVN activity in pre-clinical and clinical studies.Keywords: Anti, HIV Protein, Bacteria, Cyanovirin, N, Expression system, Transgenic plants, Yeast