فهرست مطالب
Biolmpacts
Volume:8 Issue: 3, Sep 2018
- تاریخ انتشار: 1397/05/27
- تعداد عناوین: 9
-
-
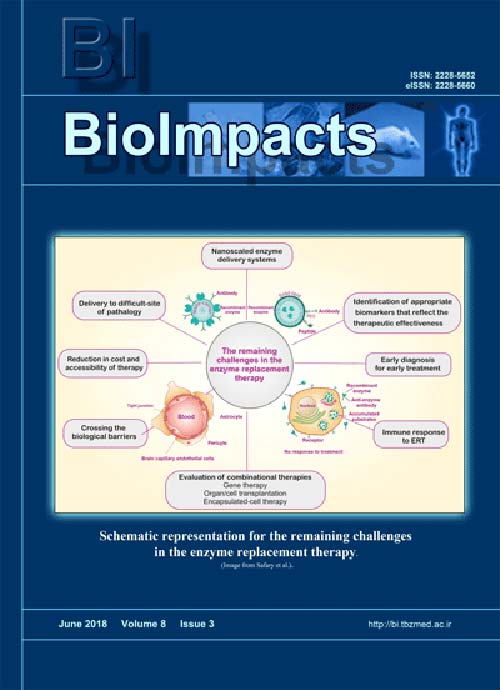
Pages 153-157Despite many beneficial outcomes of the conventional enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), several limitations such as the high-cost of the treatment and various inadvertent side effects including the occurrence of an immunological response against the infused enzyme and development of resistance to enzymes persist.
These issues may limit the desired therapeutic outcomes of a majority of the lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs). Furthermore, the biodistribution of the recombinant enzymes into the target cells within the central nervous system (CNS), bone, cartilage, cornea, and heart still remain unresolved. All these shortcomings necessitate the development of more effective diagnosis and treatment modalities against LSDs. Taken all, maximizing the therapeutic response with minimal undesired side effects might be attainable by the development of targeted enzyme delivery systems (EDSs) as a promising alternative to the LSDs treatments, including different types of mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs) as well as Fabry, Krabbe, Gaucher and Pompe diseases.Keywords: Enzyme replacement therapies, Enzyme delivery systems, Targeted delivery systems, Lysosomal storage disorders, Mucopolysaccharidoses, Krabbe disease -
Pages 159-165IntroductionObesity is commonly linked up with several life-threatening diseases. This study aims to investigate the association of fatty acid synthase (FASN) rs4246445, rs2229425, rs2228305, and rs2229422 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with the risk of overweight and obesity in the Malaysian population.MethodsBlood samples were collected from 1030 individuals who were grouped into normal, overweight, and obese categories. Blood biochemistry test and lipid profiling were performed and genomic DNA was extracted. Genotyping was performed using hydrolysis probes and odd ratio with 95% CI was calculated for risk association analysis. Linkage disequilibrium and haplotypes analyses were carried out using SHEsis software.ResultsWe found that the hemoglobin and white blood cell counts were significantly high in the obese subjects. There is a lack of evidence to link the FASN SNPs with the risk of overweight and obesity in the population. All 4 SNPs were seemed to be in linkage equilibrium. Five common haplotypes were identified in this study but none of them was significantly associated with overweight and obesity in the population.ConclusionOur findings suggest a lack of evidence to associate the FASN rs4246445, rs2229425, rs2228305, and rs2229422 SNPs with the risk of overweight and obesity in the Malaysian population. All 4 SNPs were independent of each other and not all identified haplotypes were significantly associated with overweight and obesity in this study.Keywords: Fatty acid synthase, Obesity, Overweight, Single nucleotide polymorphisms
-
Pages 167-176IntroductionDOF proteins are a family of plant-specific transcription factors with a conserved zinc finger (ZF) DNA-binding domain. Although several studies have demonstrated their specific DNA binding, quantitative affinity data is not available for the binding of DOF domains to their binding sites.MethodsZF domains of DOF2.1, DOF3.4, and DOF5.8 from Arabidopsis thaliana were expressed and purified. Their DNA binding affinities were assessed using gel retardation assays and microscale thermophoresis with two different oligonucleotide probes containing one and two copies of recognition sequence AAAG.ResultsDOF zinc finger domains (DOF-ZFs) were shown to form independently folded structures. Assessments using microscale thermophoresis demonstrated that DOF-ZFs interact more tightly (~ 100 fold) with double-motif probe than the single-motif probe. The overall Kd values for the DOF3.4-ZF and DOF5.8-ZF to the double-motif probe were ~2.3±1 and 2.5±1 µM, respectively.ConclusionStudied DOF-ZF domains formed stable complexes with the double-motif probe. Although DOF3.4-ZF and DOF5.8-ZF do not dimerize with an appreciable affinity in the absence of DNA (judging from size-exclusion and multiangle laser light scattering data), it is possible that these ZFs form protein-protein contacts when bound to this oligonucleotide, consistent with previous reports that DOF proteins can homo- and hetero-dimerize.Keywords: DOF zinc finger domain, DNA binding affinity, Gel retardation assay, Microscale thermophoresis
-
Pages 177-183IntroductionLupus nephritis (LN) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in the patients with lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease. The role of genetic and epigenetic factors is emphasized in the pathogenesis of LN. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the levels of immune-regulatory microRNAs (e.g., miR-31, miR-125a, miR-142-3p, miR-146a, and miR-155) in plasma samples of patients with LN.MethodsIn this study, 26 patients with LN and 26 healthy individuals were included. The plasma levels of the microRNAs were evaluated by a quantitative real-time PCR. Moreover, the correlation of circulating plasma microRNAs with disease activity and pathological findings along with their ability to distinguish patients with LN were assessed.ResultsPlasma levels of miR-125a (P = 0.048), miR-146a (P = 0.005), and miR-155 (PConclusionBased on the findings of the present study, the studied microRNAs may be involved in the pathogenesis and development of LN and have the potential to be used as diagnostic and therapeutic markers in LN.Keywords: Autoimmunity, Biomarkers, Circulating microRNAs, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
-
Pages 185-194IntroductionGallic acid (GA) and curcumin (Cur) are natural phenolic compounds that their anti-tumor effects on many types of cancers have been proved. In the current study, the effect of the combination of these agents on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells was investigated.MethodsInhibition of cell proliferation (MTT assay), light microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, cell cycle analysis, nitrite detection, ROS levels, measurement of the mitochondrial membrane potential, GSH level, Annexin V assay, RT-PCR and Western blotting methods were applied.ResultsThe results revealed the combination of GA and Cur strongly decreased MDA-MB-231 cell growth. Moreover, this combination increased ROS level and cytotoxic activity along with the glutathione depletion in MDA-MB-231 cells. Flow cytometry analysis showed the combination of GA and Cur increased sub-G1 cell population. Furthermore, fluorescent staining and Annexin V/PI assay showed that apoptotic cells were significantly increased in the presence of GA and Cur. At last, protein expression evaluation showed that the combination of GA and Cur significantly decreased Bcl-2 level while increased Bax, cleaved-caspase3 and PARP levels in MDA-MB-231 cells.ConclusionThese results suggest that GA in combination with Cur could be a possible candidate for chemoprevention agent of triple negative breast cancer.Keywords: Apoptosis, Breast cancer, Curcumin, Gallic acid, Mitochondria, ROS
-
Pages 195-200IntroductionThe middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired arteries that supply the blood to the cerebrum. In the present study, the three-dimensional (3D) blood flow in the left MCA was numerically simulated by using the medical imaging.MethodsThe arterial geometry was obtained by applying the CT angiography of the MCA of a 75-year-old man. The blood flow was assumed to be laminar and unsteady. Numerical simulations were done by commercial software package COMSOL Multiphysics 5.2. In this software, the Galerkins finite element method was applied to solve the governing equations.ResultsIt was found that the results obtained for the Newtonian and non-Newtonian models of blood do not differ from each other significantly. Thus, the Newtonian model for blood flow in the MCA is acceptable. Also, the most susceptible region of the MCA for Atherosclerosis was detected.ConclusionIt can be concluded that the application of the Newtonian model for the blood flowing in the MCA is acceptable. Also, atherosclerosis has the potential to occur at the middle of a branch of the MCA which has the highest geometrical curvature.Keywords: Middle cerebral artery, Hemodynamics, Non-Newtonian model, Finite element method
-
Pages 201-209IntroductionQuorum sensing inhibition (QSI) is one of the vital tools to overcome emerging virulence of pathogenic bacteria which aims at curbing bacterial resistance. Targeting QS (quorum sensing) as chemotherapy is less likely to generate resistance among pathogens as it targets only the adaptation and not the survival mechanism of the pathogen. Several QS inhibitors were developed in the recent past but none of them managed to have clinical application due to known toxic effects for human consumption. A rapid development of QS inhibitor drugs could be achieved by verification of the QSI activity of drugs which are already in clinical use with known pharmacology. Recently, a known FDA approved clinical drug niclosamide belonging to an anthelmintic class is found to exhibit QSI activity.MethodsWe have focused our study on Albendazole, another FDA approved clinical drug belonging to the same class for its potential to act as QSI. The structure-based molecular docking is used for finding putative interactions made by this drug with the CviR and LasB receptor protein of Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. Further, the in vitro activity of this drug has been evaluated by employing CviR and LasB receptor-based bioassay. The efficacy of this drug alone and in combination with antibiotic Tobramycin to inhibit P. aeruginosa based biofilms was also analyzed by developing the biofilms on chambered glass slides and performing anti-biofilm assay.ResultsFurther, this drug found to inhibit purple pigment violacein production in C. violaceum, which is under the control of C6-AHL-CviR mediated QS in this human pathogen. The in vivo bioassays results suggested that albendazole has great potential to act as a QS inhibitor as found inhibiting violacein production in C. violaceum and biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa, respectively.ConclusionIt is that structure-based molecular docking guided bioassay evaluation is an efficient tool for finding the new therapeutic use of old drugs which could have more chances to come easily in clinical application for their newly identified therapeutic uses.Keywords: Albendazole, CviR, Docking, LasR, Quorum sensing inhibitors
-
Pages 211-221IntroductionOvarian cancer is one of the most lethal gynecologic cancers. Relapses after remission are common, hence novel strategies are urgently needed. Our group has previously developed a vaccination approach based on dendritic cells pulsed with HOCl-oxidized tumor lysates. Here we investigate the improvement of this vaccine strategy using squaric acid treatment of cancer cells during tumor lysate preparation and by differentiating dendritic cells in the presence of GM-CSF and IFNα.MethodsInduction of cell death by squaric acid treatment was assessed with propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin V in ID8 tumor cells. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) immunogenic status was analyzed using a western blot-based method, as previously described. For immunological tests, ID8 cells expressing ovalbumin (ova-ID8) were treated with squaric acid before cell lysis. DCs prepared with the canonical GM-CSF and IL-4 differentiation cocktail or IFNα and GM-CSF were pulsed with tumor cell lysates and further matured in the presence of IFNγ and LPS (4-DCs and α-DCs respectively). DCs were then used in co-culture assays with ova-specific T cells and IFNγ and IL-4 secretion measured by ELISA. DC phenotypes were characterized by FACS. Finally, DCs were tested in an ovarian cancer mouse model measuring body weight and animal survival.ResultsSquaric acid treatment of mouse ovarian cancer cells induced tumor cell death as well as preserve HMGB1, a crucial Damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) signal, in its active reduced form. Squaric acid treatment of ID8-ova cells increased IFNγ and decreased IL-4 production from ova-specific T cells in co-culture experiments, promoting a more immunogenic cytokine secretion pattern. DCs differentiated in the presence of IFNα induced a considerable decrease in IL-4 production compared to canonical 4-DCs, without affecting IFNγ release. DC phenotyping demonstrated a more mature and immunogenic phenotype for IFNα-differentiated DCs. Vaccination in tumor-bearing mice showed that IFNα-differentiated DCs pulsed with squaric acid-treated lysates were the most potent at delaying tumor growth, improving animal survival.ConclusionWe identified squaric acid as a novel immunogenic treatment of tumor cells for cancer vaccines particularly efficient in prolonging animal survival when used in combination with IFNα-differentiated DCs. These promising results support future efforts for the clinical translation of this approach.Keywords: Cancer vaccine, Dendritic cells, IFNα, Ovarian cancer, Squaric acid
-
Pages 223-235IntroductionBreast cancer, as one of the major causes of cancer death among women, is the central focus of this study. The recent advances in the development and application of computational tools and bioinformatics in the field of immunotherapy of malignancies such as breast cancer have emerged the new dominion of immunoinformatics, and therefore, next generation of immunomedicines.MethodsHaving reviewed the most recent works on the applications of computational tools, we provide comprehensive insights into the breast cancer incidence and its leading causes as well as immunotherapy approaches and the future trends. Furthermore, we discuss the impacts of bioinformatics on different stages of vaccine design for the breast cancer, which can be used to produce much more efficient vaccines through a rationalized time- and cost-effective in silico approaches prior to conducting costly experiments.ResultsThe tools can be significantly used for designing the immune system-modulating drugs and vaccines based on in silico approaches prior to in vitro and in vivo experimental evaluations. Application of immunoinformatics in the cancer immunotherapy has shown its success in the pre-clinical models. This success returns back to the impacts of several powerful computational approaches developed during the last decade.ConclusionDespite the invention of a number of vaccines for the cancer immunotherapy, more computational and clinical trials are required to design much more efficient vaccines against various malignancies, including breast cancer.Keywords: Bioinformatics, Cancer, Epitope-based vaccine design, Vaccine design