فهرست مطالب
Biolmpacts
Volume:6 Issue: 3, Sep 2016
- تاریخ انتشار: 1395/08/10
- تعداد عناوین: 7
-
-
Pages 117-118Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique offers a robust label-free approach applicable in various investigations including binding affinity, specificity and kinetics of biological macromolecules (e.g., peptides, proteins and nucleotidase) and small molecules. SPR provides extremely important data on the kinetics and affinity of substances examined, through which bio-specific interaction(s) can be established by the analysis of adsorption of analyte onto the immobilized ligand(s) on a sensor-based analytical system. Due to SPR wide applications in biomedical laboratories, the aim of this editorial is to highlight the importance of SPR in affinity kinetics and ligand immobilization.Keywords: Analyte, Kinetic study, Ligand immobilization, Surface plasmon resonance
-
Pages 119-124IntroductionNephrotoxicity as a side effect caused by the immunosuppressive drug, cyclosporine-A (CsA), can be a major problem in transplant medicine. Oxidative stress may play an important role in the CsA-induced nephrotoxicity. It has been shown that the antihypertensive drug, valsartan (Val), has also renoprotective effects but, its molecular mechanism is largely unknown. In the present study, it was aimed to evaluate the Val effect in the alleviation of CsA nephrotoxicity via probable renal glutathione peroxidase (GPx) upregulation and oxidative stress decrease.MethodsThirty-two Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups based on CsA and/or Val administration: group A (Control, 1 mL/kg/day of olive oil as vehicle), group B (CsA, 30 mg/kg/day), group C (CsA喩, 30 mg/kg/day), and group D (Val, 30 mg/kg/day). After the administration period (six weeks), renal GPx expression was evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Plasma levels of GPx and 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl groups (PCG) were measured by spectrophotometer. Plasma levels of urea and creatinine were measured by an autoanalyzer.ResultsCsA treatment led to the decrease in renal expression and plasma levels of GPx in comparison to other study groups. Rats received CsA were detected to have significantly (pConclusionAdministration of Val may result in attenuating the nephrotoxic side effect of CsA via probable renal GPx upregulation, and subsequently oxidative stress decrease.Keywords: Cyclosporine, A, Glutathione peroxidase, Oxidative stress, Transplantation, Valsartan
-
Pages 125-133IntroductionThe drug-plasma protein interaction is a fundamental issue in guessing and checking the serious drug side effects related with other drugs. The purpose of this research was to study the interaction of cephalexin with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and displacement reaction using site probes.MethodsThe interaction mechanism concerning cephalexin (CPL) with BSA was investigated using various spectroscopic methods and molecular modeling method. The binding sites number, n, apparent binding constant, K, and thermodynamic parameters, ΔG0, ΔH0, and ΔS0 were considered at different temperatures. To evaluate the experimental results, molecular docking modeling was calculated.ResultsThe distance, r=1.156 nm between BSA and CPL were found in accordance with the Forster theory of non-radiation energy transfer (FRET) indicating energy transfer occurs between BSA and CPL. According to the binding parameters and ΔG0= negative values and ΔS0= 28.275 jmol-1K-1, a static quenching process is effective in the CPL-BSA interaction spontaneously. ΔG0 for the CPL-BSA complex obtained from the docking simulation is -28.99 kjmol-1, which is close to experimental ΔG of binding, -21.349 kjmol-1 that indicates a good agreement between the results of docking methods and experimental data.ConclusionThe outcomes of spectroscopic methods revealed that the conformation of BSA changed during drug-BSA interaction. The results of FRET propose that CPL quenches the fluorescence of BSA by static quenching and FRET. The displacement study showed that phenylbutazon and ketoprofen displaced CPL, indicating that its binding site on albumin is site I and Gentamicin cannot be displaced from the binding site of CPL. All results of molecular docking method agreed with the results of experimental data.Keywords: Bovine serum albumin, Cephalexin, Circular dichroism, Fluorescence spectroscopy, Gentamicin displacement, Molecular modeling
-
Pages 135-147IntroductionGrowing demands for ultrasensitive biosensing have led to the development of numerous signal amplification strategies. In this report, a novel electrochemiluminescence (ECL) method was developed for the detection and determination of caspase-3 activity based on reduced graphene oxide sheets decorated by gold nanoparticles as signal amplification element and horseradish peroxidase enzyme (HRP) as ECL intensity enhancing agent.MethodsThe ECL intensity of the luminol was improved by using the streptavidin coated magnetic beads and HRP in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The cleavage behavior of caspase-3 was characterized by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) techniques using biotinylated peptide (DEVD containing peptide) which was coated on reduced graphene oxide decorated with gold nanoparticle. The surface modification of graphene oxide was successfully confirmed by FTIR, UV-vis and x-ray spectroscopy.ResultsECL based biosensor showed that the linear dynamic range (LDR) and the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) were 0.5-100 and 0.5 femtomolar (fM), respectively. Finally, the performance of the engineered peptide based biosensor was validated in the A549 cell line as real samples.ConclusionThe prepared peptide based biosensor could be considered as an excellent candidate for early detection of apoptosis, cell turnover, and cancer related diseases.Keywords: Apoptosis, Caspase, 3, DEVD, peptide, Electrochemiluminescence, Gold nanoparticle, Reduced graphene oxide
-
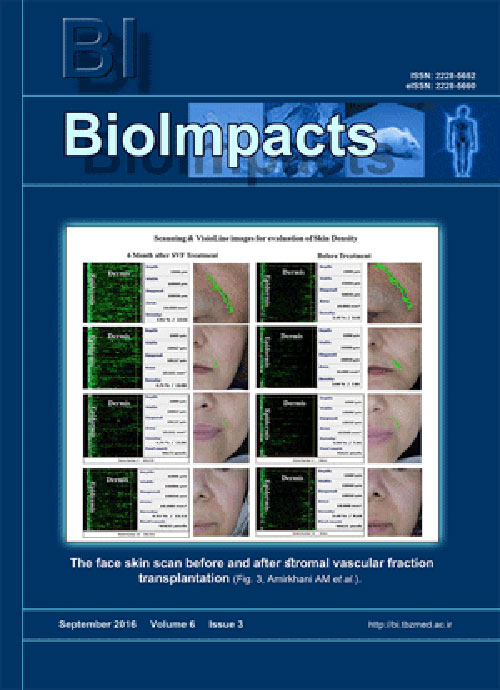
Pages 149-154IntroductionThe rejuvenation characteristics of fat tissue grafting has been established for many years. Recently it has been shown that stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of fat tissue contributes to its rejuvenation properties. As the SVF is a minimal processed cell population (based on FDA guidance), then it is a suitable cell therapy for skin rejuvenation. This clinical trial was aimed to evaluate the ultrastructural improvement of aging skin in the facial nasolabial region after transplantation of autologous SVF.MethodsOur study was conducted in 16 patients aged between 38 and 56 years old that were interested in face lifting at first. All of the cases underwent the lipoaspiration procedure from the abdomen for sampling of fat tissue. Quickly, the SVF was harvested from 100 mL of harvested fat tissue and then transplanted at dose of 2.0×107 nucleated cells in each nasolabial fold. The changes in the skin were evaluated using Visioface scanner, skin-scanner DUB, Visioline, and Cutometer with multi probe adopter.ResultsBy administration of autologous SVF, the elasticity and density of skin were improved significantly. There were no changes in the epidermis density in scanner results, but we noticed a significant increase in the dermis density and also its thickness with enrichment in the vascular bed of the hypodermis. The score of Visioface scanner showed slight changes in wrinkle scores. The endothelial cells and mesenchymal progenitors from the SVF were found to chang the architecture of the skin slightly, but there was not obvious phenotypic changes in the nasolabial grooves.ConclusionThe current clinical trial showed the modification of dermis region and its microvascular bed, but no changes in the density of the epidermis. Our data represent the rejuvenation process of facial skin by improving the dermal architecture.Keywords: Cell therapy, Dermatology, Facial skin, Regenerative medicine, Rejuvenation, SVF
-
Pages 155-167IntroductionElaeagnus spp. is one in the family of riparian trees growing near the rivers or water corridors. In this family, Elaeagnus angustifolia (Russian olive) is famous because of its medical applications.MethodsA comprehensive review was performed to extract the related data from published literature.ResultsTraditionally, it has been used as an analgesic, antipyretic and diuretic herbal medicine. A large number of compounds have been derived from Russian olive and made this plant a source of flavonoids, alkaloids, minerals and vitamins. Although the purpose of most studies is to use this plant for preparation of herbal medicines and as an ingredient for drug formulation, there is no available drug dosage form commercially.ConclusionThis review aimed to provide the most important documentary information on the active components of Elaeagnus spp. and their relation to the pharmacological properties and compare them with reported medicinal effects.Keywords: Elaeagnus angustifolia, Russian olive, Inflammation, Traditional remedy, Flavonoid
-
Pages 169-179IntroductionGrowing advances in nanotechnology have facilitated the applications of newly emerged nanomaterials in the field of biomedical/pharmaceutical sciences. Following this trend, the multifunctional nanoparticles (NPs) play a significant role in development of advanced drug delivery systems (DDSs) such as diapeutics/theranostics used for simultaneous diagnosis and therapy. Multifunctional radiolabeled NPs with capability of detecting, visualizing and destroying diseased cells with least side effects have been considered as an emerging filed in presentation of the best choice in solving the therapeutic problems. Functionalized magnetic and gold NPs (MNPs and GNPs, respectively) have produced the potential of nanoparticles as sensitive multifunctional probes for molecular imaging, photothermal therapy and drug delivery and targeting.MethodsIn this study, we review the most recent works on the improvement of various techniques for development of radiolabeled magnetic and gold nanoprobes, and discuss the methods for targeted imaging and therapies.ResultsThe receptor-specific radiopharmaceuticals have been developed to localized radiotherapy in disease sites. Application of advanced multimodal imaging methods and related modality imaging agents labeled with various radioisotopes (e.g., 125I, 111In, 64Cu, 68Ga, 99mTc) and MNPs/GNPs have significant effects on treatment and prognosis of cancer therapy. In addition, the surface modification with biocompatible polymer such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) have resulted in development of stealth NPs that can evade the opsonization and immune clearance. These long-circulating agents can be decorated with homing agents as well as radioisotopes for targeted imaging and therapy purposes.ConclusionThe modified MNPs or GNPs have wide applications in concurrent diagnosis and therapy of various malignancies. Once armed with radioisotopes, these nanosystems (NSs) can be exploited for combined multimodality imaging with photothermal/photodynamic therapy while delivering the loaded drugs or genes to the targeted cells/tissues. These NSs will be a game changer in combating various cancers.Keywords: Nuclear imaging, PET, SPECT, Radiolabeled nanoparticles, Theranostics