فهرست مطالب
Pharmaceutical Sciences
Volume:25 Issue: 2, Jun 2019
- تاریخ انتشار: 1398/04/08
- تعداد عناوین: 14
-
-
Pages 85-92Protein and peptide delivery systems attract great attention nowadays. They play crucial role in several diseases, but their way of administration has some disadvantages that makes patients dissatisfied. In this study, we choose insulin as a peptide that is used for type I and type II diabetic patients, but injection way of its usage is not suitable in diabetes as a chronic remedy. Although oral way is a needle-free one, but its bioavailability through that would be decreased because of degradation in gastro-intestine and consequently, further dosage should be used to get the desired hypoglycemic effect. Administration of insulin through non-parenteral and less enzymatic pathways, such as intranasal, pulmonary, transdermal, colon and vaginal routes, is new that attracts researchers’ attention considerably. Although the bioavailability of insulin may be lower than the current injection way, but it may be improved by some strategies like the use of permeation enhancers. There are also some limitations in each way, but propagation of them would result in improvement of patients’ quality of life and may cause some economic profits. The objective of this review was to introduce the convenient ways for long term insulin administration with few enzymatic barriers.Keywords: Insulin, Delivery ways, Non- invasive, Less enzymatic
-
Pages 93-99BackgroundVanadium is a potential neurotoxic agent widely distributed in the environment. Understanding the neurotoxic mechanisms of vanadium on learning and memory seems necessary.MethodsWe investigated the time-dependent (1-week, 2- week and 4-week) effects of sodium metavanadate (SMV) (25 mg/kg/day; pre-training oral administration) and 4-day intraperitoneal injections of aminoguanidine (AG) as a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (10, 50, and 100 mg/kg) on spatial memory retention in Morris water maze. Animals were trained for 4 days and tested 48 h after the last training trial.ResultsThe data showed that 4-week oral pre-treatment with SMV (25 mg/kg/day) induced spatial memory retention deficits and decreased the time spent in the target quadrant. We found that 4-day administration of different doses of AG during training trials significantly decreased the time and distance of finding the hidden platforms. Additionally, SMV-induced spatial memory retention impairments were prevented in animals received combined SMV (25 mg/kg/day, 4 weeks) and AG (10 mg/kg/day, 4 days).ConclusionOur findings showed the protective role of AG on SMV-induced spatial memory retention deficits.Keywords: Sodium metavanadate, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase, Morris water maze, Spatial memory
-
Pages 100-110BackgroundAstragaloside IV (AST) is a saponin from the roots of Astragalus plants which has been widely used in traditional medicine to treat cardiovascular diseases. However, the effect of AST on myocardial infarction remains unknown. Thus, we aimed to investigate the cardio protective effects of AST on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats.MethodsAST was isolated from the roots of Astragalus caspicus. Male Wistar rats were assigned to 5 groups of control, isoproterenol, and treatment with 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/kg AST given orally immediately before MI induction. Subcutaneous injection of isoproterenol (100 mg/kg) for two consecutive days was used to induce myocardial infarction. AST was given orally once daily for 4 days. On the fifth day hemodynamic and electrocardiographic parameters were assessed, and serum and tissue samples were used to evaluate histological and biochemical changes. To more assessment of the effects of AST on myocardium, we also used three doses of 0.1, 1 and 2 µM of AST in isolated heart model. In statistical analysis with one-way-ANOVA test, any differences between groups were considered significant at p<0.05.ResultsIsoproterenol injection caused ECG abnormality, hemodynamic depression and myocardium damage. While AST administration increased mean arterial blood pressure and heart rate and improved the left ventricular contractility. The peripheral neutrophil count, cardiac enlargement and cardiac ischemia was significantly decreased by AST. Also, histopathological evaluations showed that AST significantly diminished post MI necrosis and fibrosis in heart tissue and inhibited the inflammatory responses. The isolated heart studies hemodynamic factors showed no significant changes.ConclusionResults showed that AST can protect heart against myocardial infarction by improving cardiac histology and ventricular contractility. Due to the lack of protection in the isolated heart, it is likely that the positive effects are more associated with the improvement of the oxidative stress markers in the systemic circulation, and the absolute effect on the isolated heart does not play an essential role in myocardium protection.Keywords: Astragaloside IV, Myocardial infarction, Isoprotrenol, Oxidative stress, Isolated heart
-
Pages 111-117BackgroundHepatotoxicity—the most important side effect of the Methotrexate (MTX)—seems to relate to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Pomegranate has high anti-oxidant capacities. We studied if MTX-induced hepatotoxicity can be protected by pomegranate peel and seed methanolic extracts (PPE and PSE) in rats.MethodsForty-eight Wistar rats were divided on the basis of: orally received normal saline as control, orally received 500 mg/kg PSE, orally received 500 mg/kg PPE, intramuscularly (IM) received 10 mg/kg MTX, MTX- and PSE-received, and MTX- and PPE-received groups. After the intervention, blood and liver samples were obtained.ResultsThe results showed considerable antioxidant activity (510.7 ± 2.5 µg/ml) and total phenolic content (147.2 ± 0.2 mg GAE/g extract) of PSE and PPE, respectively. The ALT value reached the levels of the control group after treatment with PSE in PSE + MTX group. The serum level of ALT showed a significant increase in PPE+MTX group in comparison with MTX group. The results indicated that the PSE and PPE did not have considerable effect on ALP levels alone or together with MTX. Our results showed that PSE+ MTX and also PPE+ MTX treatment caused serum AST values to increase significantly in comparison with control and MTX groups. In histopatological study, the extracts decreased the pathological changes induced by methotrexate.ConclusionThe present study demonstrated that PPE and PSE that have notable total flavonoid and phenolic contents and also antioxidant activity, can protect the liver against histo-pathological and some enzymatic changes induced by MTX in rats.Keywords: Hepatotoxicity, Methotrexate, Pomegranate, Rat
-
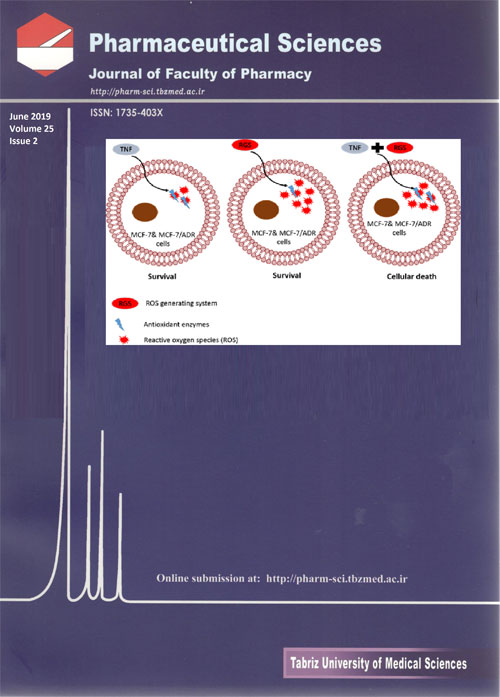
Pages 118-123BackgroundSignal transduction of numerous cytokines and growth factors are mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) have stimulated accumulation of ROS in various in vitro studies. MCF-7 and its Adriamycin resistant variant MCF-7/ADR are resistant against TNF-α cytotoxicity. Role of ROS in the resistance of MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR cells was investigated.MethodsROS accumulation and viability in MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR after TNF-α exposure was evaluated using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) as a fluorescent probe and 3-[4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2, 5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) cytotoxicity assay respectively.ResultsROS level did not change significantly after TNF-α exposure. Induction of ROS accumulation along with TNF-α treatment sensitized these cells to TNF-α toxicity.ConclusionIt can be concluded that lack of ROS accumulation following TNF-α exposure is involved at least by part in the resistance of MCF-7 and its drug resistant derivative MCF-7/ADR cells to TNF-α cytotoxicity.Keywords: Breast cancer, MCF-7, Multidrug resistance, ROS, TNF-α
-
Pages 124-131BackgroundTapinanthus globiferus (A. Rich) Teigh. (Loranthaceae) is an excellent medicinal plant in terms of efficacy and also traditionally used for the treatment of various diseases including inflammations, cancer, diabetes and strokes. This study was designed to assess the anti-inflammatory activity of the leaf extracts of T. globiferus in wistar rats and identify phytochemical constituents of the extracts responsible for the observed activity.MethodsTapinanthus globiferus leaves was extracted with hexane, ethyl acetate and methanol in a soxhlet apparatus. The extracts were subjected to qualitative phytochemical analysis, toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity using carrageenan-induced paw oedema in wistar rats. Piroxicam (20 mg/kg) was used as reference standard. The data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance with significant level set at p≤0.05.ResultsThe percentage yield from the gradient extraction of T. globiferus leaves showed methanol to be the highest and the chromatographic analysis visualized with specific reagents confirmed the presence of steroids/triterpenes, phenolic compounds and flavonoids in the leaf of T. globiferus. LD50 was above 2,000 mg/kg and no death was recorded. The hexane, ethyl acetate and methanol leaf extracts of T. globiferus at 250, 500 and 1,000 mg/kg produced a significant decrease in paw oedema (p≤0.05) with percentage inhibition at the first and third hour for hexane, ethyl acetate and methanol extract respectively. The methanol extracts recorded the highest inflammatory inhibition percentage.ConclusionThese finding revealed that the leaf of T. globiferus has anti-inflammatory activity and this justified its traditional use in the treatment of inflammation.Keywords: Tapinanthus globiferus, Carrageenan, TLC, Acute toxicity
-
Pages 132-137BackgroundNitric oxide and reactive nitrogen species play an important role in various pathological conditions like cancer, inflammation and neurodegeneration. As plants and natural compounds have a great potency of discovering lead compounds which might affect NO production during inflammation and various pathologies, we examined the effects of three medicinal plants native to Iran, on NO production during oxidative stress in PC12 cells.MethodsIn this study, cell death and NO levels were measured by MTT and by Griess assay, respectively. Oxidative stress was induced by hydrogen peroxide and extracts of Astragalus jolderensis, Convolvulus commutatus and Salvia multicaulis were used as pretreatment in oxidative stressed PC12 cells.ResultsA. jolderensis extract significantly suppressed NO production in 150 and 200 μg/ml concentrations and C. commutatus extract in all concentration inhibited NO production in stressed PC12 cells. In addition, the extract of S. multicaulis inhibited NO production during stress at all concentrations above 50 μg/ml. Besides, the extract of S. multicaulis showed protective effect at lower doses in stressed cells.ConclusionAccording to the results, S. multicaulis inhibited NO production and protected cells from oxidative stress. Hence, S. multicaulis is a good candidate for further in vitro and in vivo investigations. A. jolderensis and C. commutatus also suppressed NO production during stress. Therefore, they could be noticed in experiments that centralize on the inhibition of NO production and drug discovery studies in the field of neurodegenerative and chronic inflammatory diseases.Keywords: Nitric Oxide, PC12, Astragalus jolderensis, Convolvulus commutatus, Salvia multicaulis, Griess assay
-
Pages 138-144BackgroundDifferent endemic species of Apiaceae that widely grow in Hyrcanian region have long been used as spices and herbal remedies. Chemical compositions and bioactivity of many of these plants have not been studied scientifically. The volatile constituents and antimicrobial activity of four edible Apiaceae plants—Elaeosticta glaucescens Boiss, Malabaila secacul (Mill.) Boiss, Caucalis platycarpos L., and Eryngium caucasicum Trautv—roots were investigated.MethodsGas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC–MS) and gas chromatography/flame ionization detection (GC–FID) methods were used for chemical investigation. Antimicrobial potential of the volatile compositions of these roots were investigated using the disc diffusion method on four microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacillus subtilis.ResultsThe best minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of these species were revealed for B. subtilis and S. aureus (500 µg/mL for MIC and MBC) followed by E. caucasicum and C. platycarpus, respectively. The main compounds of E. caucasicum root essential oil were hexyl isovalerate (11.0%) and hexyl valerate (10.1%). E. glaucescens root essential oil was mainly composed of 3(10)-caren-4-ol, acetoacetic acid ester (9.8%), octyl isovalerate (8.9%), and octyl acetate (5.7%). In C. platycarpos root, hexyl isovalerate (9.2%) and n-octyl isobutyrate (8.5%) were constituted the major compositions of the essential oil while n-hexyl isobutyrate (8.5%) and hexyl hexanoate (7.8%) were predominant compounds in M. secacul.ConclusionThe essential oils of E. caucasicum and C. platycarpus roots were contained high amount of short chain fatty acid esters (SCFAE) and trans- pinocarvyl acetate. They exhibited moderate antibacterial activity.Keywords: Apiaceae, Eryngium caucasicum, Elaeosticta glaucescens, Malabaila secacul, Caucalis platycarpos, Essential oils, Antimicrobial activity, Food borne bacteria
-
Pages 145-153BackgroundSnakehead fish (Ophiocephalus striatus) is a freshwater fish that is utilized as anti-inflammatory and anticancer drug. The aim of this study was to determine the toxicity effect of snakehead fish powder (SFP), formulate it into liposome and in vitro study using sensitive and resistant breast cancer cells.MethodsDried powder of snakehead fish was made using the atomizer then made a test solution which was divided into 7 treatment groups in different concentrations. They were exposed to zebrafish embryos then observed for 72 h post fertilization (hpf). After acquiring the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and lethal concentration (LC50) of SFP, these concentrations were used to formulate SFP into liposome by extrusion method. SFP-liposomes were characterized and stable tested. Afterwards, SFP-liposomes were evaluated in vitro using sensitive and resistant breast cancer cells.ResultsThe maximum allowed toxicant concentration of SFP was 0.0543 mg/mL meaning slight toxic symptoms, IC50 = 0.0945 mg/mL showing the growth inhibition of zebrafish embryos, and LC50 = 0.1549 mg/mL meaning very toxic category that has killed zebrafish embryos. The characterization results showed that size of SFP-liposome were 121 nm ± 0.29, polydispersity index 0.06 ± 0.02, zeta-potential -10.15 mV ± 0.36 and % entrapment efficiency (EE) 85.75% ± 2.24. Six weeks of stability study showed that size profile was stable at 25°C and 37°C. Moreover, SFP-liposomes inhibited breast cancer cell proliferation when evaluated with 4T1 and MDA-MB231-sensitive and resistant cells.ConclusionSFP has bioactive compounds based on toxicity effect and can be formulated into liposome as a promising nanonutraceutical formulation.Keywords: Liposome, Powder, Resistant cell, Snakehead fish, Toxicity effect, Zebrafish
-
Pages 154-164BackgroundThe thermophysical properties of 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium salicylate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient based on ionic liquid have been investigated in the presence of aqueous solutions of glycine. Therefore, the scope of this article was to determine these properties by measuring the densities, speeds of sound, viscosities, electrical conductances and refractive indices for ternary (glycine + 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium salicylate + water) soloutions at T = 298.15 K.MethodsA commercial density and speed of sound measurement apparatus was used to measure the density and speed of sound data. Viscosities, electrical conductivities and refractive indices of the studied solutions were measured using digital viscometer, conductivity meter and refractometer, respectively.ResultsVariety of properties such as partial molar volume of transfer , partial molar isentropic compressibility of transfer , viscosity B-coefficients of transfer , ion association constants (KA) and molar refraction RD were determined to investigate the solute-solute and solute-solvent interactions in these systems.ConclusionThe positive values of transfer properties including partial molar volume of transfer ( ), partial molar isentropic compressibility of transfer ( ), and viscosity B-coefficients of transfer (∆traB) indicated that in these systems, the ion-polar and polar-polar interactions are dominant. The calculated hydration number showed that dehydration of glycine occurs in presence of this ionic liquid.Keywords: 1-octyl-3-methylimidazoliumsalicylate, Viscosity b-coefficient, Hydration number, Molar conductivity
-
Pages 165-170BackgroundRecently Sandeepa et al. reported the solubility of benzoic acid in six monosolvents (i.e. tributyl phosphate, diacetone alcohol, methyl-n-propyl ketone, methyl acetate, amyl acetate, and isooctane) and five binary systems (i.e. ethanol + hexane, isopropyl alcohol + hexane and chloroform + hexane, acetone + hexane, and acetone + water) along with some numerical analyses. The reported calculations have been reanalyzed and some recommendations and further computations were proposed.MethodsFurther analyses were performed based on combined nearly ideal binary solvent/Redlich-Kister, the modified Wilson model, general single model, Jouyban–Acree model and Jouyban–Acree–van’t Hoff model.ResultsThe mentioned numerical analyses were used to predict the solubility of benzoic acid in the binary solvent mixtures at various temperatures and the predicted solubility data were compared with their corresponding experimental values by calculating relative deviations.ConclusionThe investigated models provide good estimation of the solubility behavior of benzoic acid in the binary solvent mixtures at various temperatures.Keywords: Benzoic acid, Solubility prediction, Binary solvent mixtures
-
Pages 171-175BackgroundArtemisia ciniformis (A. ciniformis) belongs to the genus Artemisia and grows at northeast of Iran. The current phytochemical study was carried out on the most potent extract in cell-free antioxidant assays.MethodsHydroethanolic extract of the aerial parts was fractionated using vacuum-liquid chromatography (VLC). The selected fraction from the previous cell-free antioxidant study was purified by semi-preparative HPLC. The structures of isolated compounds were identified using one- and two-dimensional NMR and ESIMS techniques.ResultsThree identified compounds in this study were the known isomers of dicaffeoylquinic acid (DCQ), including 3,5- DCQ (isochlorogenic acid A), 3,4-DCQ (isochlorogenic acid B) and 4,5-DCQ (isochlorogenic acid C).ConclusionThe outstanding free radical scavenging potential in the hydroethanolic extract of A. ciniformis might be partly related to the presence of isochlorogenic acid derivatives.Keywords: Artemisia ciniformis, Dicaffeoylquinic acid, Isochlorogenic acid, Antioxidant activity