فهرست مطالب
Pharmaceutical Sciences
Volume:25 Issue: 4, Dec 2019
- تاریخ انتشار: 1398/11/05
- تعداد عناوین: 13
-
-
Pages 278-286
Tramadol is a widely used opioid analgesic frequently prescribed for treatment of moderate to severe, acute and chronic pain. It has a complex mechanism of action, acting both as a central opiate agonist and as a norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitor. It is a chiral substance, having two chiral centers in its structure and it is used in therapy as a racemic mixture of two of its enantiomers, (S,S)-tramadol and (R,R)-tramadol. In the last 25 years, several analytical procedures have been published in the literature for the achiral and chiral determination of tramadol from pharmaceutical formulations and biological matrices. Among these methods, capillary electrophoresis techniques have proved to be an efficient, reliable and cost-effective solution. The purpose of the present review is to provide a systematic survey to present and discuss the electrodriven methods available in the literature for the achiral and chiral analysis of tramadol.
Keywords: Tramadol, Capillary electrophoresis, Chiral separation, Pharmaceutical analysis -
Pages 287-293Background
According to the previous studies, the exact mechanism of dependence on opioids and withdrawal syndrome has not been fully understood but one of the most important mechanisms is the increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines in CNS. On the other way, previous studies showed that natural honey (NHO) has anti-inflammatory properties. This study was aimed to evaluate the effects of chronic administration of natural honey on the development of morphine dependence in male rats.
MethodsHoney was prepared from Tarom Oliya region in Zanjan province. Experiments were performed on male Wistar rats weighing 225-275 g, randomly divided into 6 groups (n=8). The study groups included morphine group, the three doses of morphine plus honey group (at doses of 200,400 and 800 mg/kg, i.p.), the morphine plus vehicle group, and the saline group. The subcutaneous injections of additive doses of morphine were used for 9 days to create morphine dependency. On the 9th day, one hour after the morning dose of morphine, naloxone (4 mg/kg, i.p.) was injected, and symptoms of withdrawal syndrome were assessed for 60 minutes. Then, blood samples were taken to measure TNF-α. Oneway ANOVA and Tukey tests were used to compare the results. P- Value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
ResultsThe results of this study showed that intraperitoneal injection of honey at 3 doses (200, 400 and 800 mg/kg with p <0.001) could significantly decrease the total score of the symptoms compared to the morphine-vehicle control group. Natural honey (NHO) could significantly decrease TNF-α at dose of 400 mg/kg.
ConclusionThe results indicated that chronic administration of NHO had beneficial effects in reducing symptoms of morphine withdrawal syndrome, and this effect is probably due to the anti-inflammatory effect caused by the polyphenolic compounds in honey.
Keywords: Morphine, Dependency, Withdrawal Syndrome, Natural Honey, Total Withdrawal Score, TNF-α -
Pages 294-302Background
The oleo-gum-resin of Commiphora myrrha (myrrh) has a long history of therapeutic use in traditional medicine. The aim of this study was to seek for the scientific evidence to determine whether the ethanolic extract of myrrh (EEM) has any beneficial effects on Streptozotocin (STZ) induced testicular impairments, and explore the possible mechanisms underlying such actions.
MethodsForty-eight severe and complicated diabetic rats (fasting blood glucose above 350 mg/dL), randomly were divided into six equal groups (n=8). Besides, eight healthy rats allocated as a normal control group and only treated with vehicle solution. The diabetic animals orally received the extract (100, 200, 300, and 500 mg/kg), metformin (500 mg/kg) or vehicle solution for 28 days. As a final point, plasma glucose and insulin, circulatory sex hormones, sperm parameters including sperm concentration, motility and viability and also testicular malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were assessed. Furthermore, quantitative histological evaluation of seminiferous tubules area and determination of germinal cells apoptosis were performed.
ResultsNone of the studied doses of EEM showed anti-diabetic effects. However, the extract mainly at the maximum dose (500 mg/kg) exhibited beneficial effects on reproductive impairments. The EEM treated rats mainly at 500 mg/kg had significantly higher sperm concentration, sperm motility, sperm viability, sex hormones and lower testicular MDA and germ cell apoptosis index than untreated diabetic rats.
ConclusionThese results indicated that EEM may have beneficial effects against reproductive dysfunction induced by diabetes. The mechanisms behind the effects might be associated with the EEM sex hormone booster potential, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties.
Keywords: Apoptosis, Commiphora myrrha, Diabetes, Sperm, Testis -
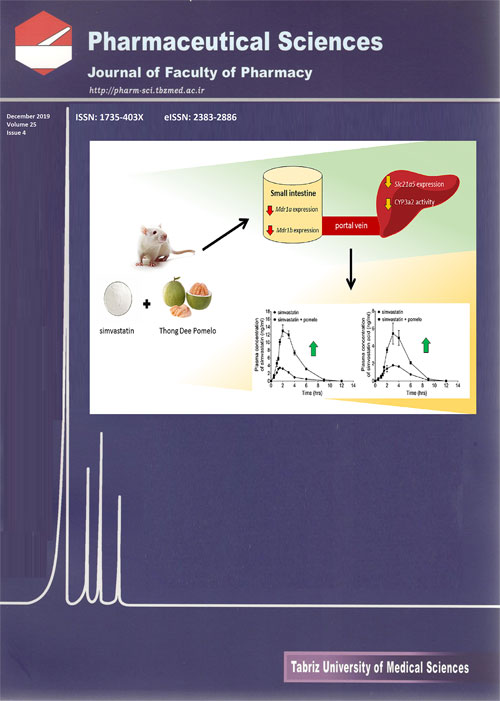
Pages 303-310Background
Food-drug interaction can decrease drug effectiveness or increase risk of drug toxicity. Simvastatin is widely used for treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of pomelo juice on the pharmacokinetics of simvastatin, CYP3a2 activity and Mdr1a, Mdr1b and Slc21a5 expressions in rats.
MethodsRats were divided into 4 groups including (i) control, (ii) pomelo that received pomelo juice orally twice daily for 7 days, (iii) simvastatin that received simvastatin on day 8, and (iv) simvastatin + pomelo juice. Plasma concentrations of simvastatin and simvastatin acid were analyzed using LC-MS/MS. Hepatic CYP3a2 activity was evaluated using midazolam hydroxylation assay. The expressions of hepatic and intestinal Mdr1a, Mdr1b and Slc21a5 were measured using the real-time RT-PCR.
ResultsOral administration of pomelo juice for 7 days altered pharmacokinetic profiles of simvastatin and its primary active metabolite, simvastatin acid, in rats. Real-time RTPCR analysis revealed that pomelo juice significantly suppressed the expression of intestinal Mdr1a and Mdr1b and hepatic Slc21a5. Rat hepatic CYP3a2 catalytic activity was also inhibited following pomelo juice administration.
ConclusionThe results of this study suggested that there was a risk of potential drug interaction associated with inhibition of drug transporters and CYP3A caused by pomelo juice.
Keywords: Drug, Food, Interaction, Rat, Simvastatin, Simvastatin acid -
Pages 311-318Background
Isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN) is used for treating the angina attacks. In addition, oral ISDN is available in immediate and sustained release formulations and the bioavailability of ISDN is about 20-25% when taken orally. Further, the ISDN films are developed for sublingual drug delivery by improving drug bioavailability. The present study aimed to design and evaluate the physicochemical properties of the film formulation for sublingual delivery of ISDN.
MethodsIn the present study, sublingual films were prepared by the solvent casting technique using the hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) polymers (i.e., 100, 150 and 200 mg) with a different drug to polymer ratios (i.e., 1:5, 1:7.5 and 1:10). Then, ISDN was evaluated for the film appearance, drug content, surface pH, mucoadhesion force, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), in vitro drug release, and ex vivo permeability.
ResultsBased on the results, F3 formulation (1:10 ISDN to HPMC ratio) showed acceptable thickness (0.93 mm), weight (11.14 mg), surface pH (7.82), moisture absorption capacity (6.08%), elasticity (>200), mucoadhesion force (18.05 N/cm2 ), and drug content (6.22%). Furthermore, the results demonstrated that HPMC polymer improved the characteristics of the films, modified the bioadhesiveness, and finally, enhanced elasticity. However, DSC thermogram failed to show any crystalline drug substance in the films except for F1 (immediate release) and the endothermic peak of ISDN was absent in F2 and F3 films. Therefore, the drug which was entrapped into the film was in an amorphous or disturbed-crystalline phase of the molecular dispersion or dissolved in the melted polymer in the polymeric matrix. Moreover, the drug release from the films was faster compared to the tablet® (P<0.05).
ConclusionIn general, the formulation of F1 was observed to be an appropriate candidate for developing the sublingual film for the remedial use.
Keywords: Film, Sublingual, Isosorbide dinitrate, HPMC, Mucoadhesion -
Pages 319-330Background
Saccharides are considered as abundant, cheap and renewable starting materials for chemicals and fuels. Recently, ionic liquids have been used as green solvents for saccharides. The solubility values of galactose in aqueous ionic liquid solutions are not available. Thus, the main objective of this research was to determine the solubility of galactose in aqueous solutions containing ionic liquids, 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium bromide, [BMIm]Br, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [BMIm]Cl and 1-hexyl-3- methyl imidazolium bromide, [HMIm]Br at different mole fractions of ionic liquids at T = (298.15 and 308.15) K.
MethodsIn this study, the gravimetric method was used to measure the solubility of galactose in aqueous ionic liquids solutions.
ResultsThe solubility values of galactose in water and aqueous ionic liquid solutions were correlated with the activity coefficient models of Wilson, NRTL, modified NRTL, NRFNRTL, and UNIQUAC.
ConclusionIt was concluded that with increasing the mole fraction of ionic liquids, the solubility values of galactose decrease and in fact all of these ionic liquids show saltingout effect on aqueous galactose solutions and this behavior is stronger in ionic liquid 1- butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride.
Keywords: Solubility, Galactose, Ionic liquid, Activity coefficient models -
Pages 331-337Background
Loading of poorly water-soluble drugs on the porous materials has attracted great interest as an effective approach for enhancement of dissolution rate of drugs. The Aerosil (Ae) with porous structure is expected to facilitate the dissolution of drugs which is generally associated with precipitation. Thus, the purpose of this investigation was thus to develop a formulation which combines a precipitation inhibitor and a poorly soluble drug loaded Ae.
MethodsA poorly water-soluble drug, Cinnarizine (CNZ) was used as a model, and Eudragit L100 (Eu) was used as a precipitation inhibitor. Formulations were produced by solvent evaporation and characterized by FT-IR and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Dissolution experiments were carried out in phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) under nonsink conditions.
ResultsDSC thermograms revealed that no crystalline structure of CNZ was present in CNZ-loaded Ae formulations and no long-range order was arranged upon loading of CNZ into Ae. In dissolution test, the CNZ-loaded Ae physically blended with Eu achieved a remarkedly higher CNZ concentration over the plain CNZ and over the CNZ-Eu co-loaded Ae. The dissolution rate of CNZ from the CNZ-loaded Ae was enhanced with increasing Ae amount and the dissolution was maximum when the ratio of CNZ: Ae was 1:10 CNZ: Ae. In addition, the precipitation inhibition was increased when the amount of Eu was high.
ConclusionThe results of this work revealed that the dissolution behaviour of CNZloaded Ae is enhanced by physically blending of Eu as a suitable precipitation inhibitor.
Keywords: Precipitation inhibitors, Cinnarizine, Aerosil, Mesoporous -
Pages 338-344Background
Acrylamide is a known carcinogenic product that has been found among the substances such as potato chips which to be processed under the heat-treatment. In order to extract amounts of acrylamide from fried chips in market, an ultrasound-assisted liquid– liquid extraction (UA-LLE) technique is proposed. The UA-LLE coupled LLE and ultrasonication in a single step.
MethodsChips samples were dissolved in an extracting organic solvent using ultrasonication to prompt transferring of acrylamide into the organic phase. As a result, the extraction time and process efficiency were significantly enhanced through increasing the collision power and mass transfer between grounded chips and organic phase.
ResultsImportant parameters affecting the extraction efficiency such as kind of organic solvent and its volume, re-dissolving solvent and pH were optimized. This newly proposed method has been applied to determine the trace acrylamide in potato chips samples purchased from local market.
ConclusionUA-LLE is a handy, economic and time-saving method, with high extraction yield (over 103% average recovery) and good precision (lower than 15% relative standard deviation, RSD). Most importantly, it seems this method to be an ideal pre-treatment method for the extraction of acrylamide in food matrix in food quality control laboratories.
Keywords: -Acrylamide, Liquid–Liquid Extraction, Potato Chips, Ultrasound -
Pages 345-351Background
Quantitative analyses of antiepileptic drugs are required in clinic and to rational dosage adjustment, the clinician needs the blood levels of these drugs. A highperformance liquid chromatography with spectrophotometric detection has been developed and validated for simultaneous determination of some antiepileptic drugs in plasma of patients with epilepsy.
MethodsA simple procedure based on deproteinization by acetonitrile was used for pretreatment of plasma samples. Liquid chromatographic analysis was carried out on a NovaPak® C18 analytical column, using a ternary mixture of potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 6.0)-acetonitrile-2-propanol (63:22:15, v/v/v) as the mobile phase, at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min-1 .
ResultsCalibration curves were linear over a range of 1–40 µg mL-1 for phenobarbital, 1– 30 µg mL-1 for phenytoin, 0.3–15 µg mL-1 for carbamazepine and 0.5–6 µg mL-1 for carbamazepine epoxide.
ConclusionThe simple sample pre-treatment, combined with the fast chromatographic run was used for the determination of antiepileptic drugs for a large number of patient samples.
Keywords: -Phenobarbital, Carbamazepine, Carbamazepine metabolite, Phenytoin, HPLC analysis, Therapeutic drug monitoring -
Pages 352-357Background
Ioversol (IVL) is a radiographic contrast agent employed in the diagnostic radiography. In this investigation, our aim was to develop and validate a simple and rapid HPLC-DAD method for determination of IVL in bulk and injection dosage form.
MethodsIVL separation and analysis was performed on Zodiac phenyl C18 column (250 mm × 4.5 mm; 5 µ particle size) using water-methanol (90:10 by volume) as mobile phase system and with detection at 254 nm.
ResultsThe retention value of IVL was 4.11 min. The method linearity range was found 254.5-763.5 µg/ml with LOQ and LOD values of 2.376 µg/ml and 0.729 µg/ml, respectively. The accuracy (̴100%) and precision (< 2.0%) were within the acceptance criteria. Stability indicating ability of the method was proved by stress degradation studies. Adoptability of this method was assessed with application to marketed injection dosage form with good accuracy (recovery 100.49%) and precision (RSD 0.715%).
ConclusionBy adopting this method one can analyze IVL in injection dosage form in less than 10 min and hence this method is time saving and enables the estimation of large number of samples.
Keywords: Ioversol-Optiray, Stability indicating, HPLC, Diode array, Analysis -
Pages 358-363Background
Piper species are aromatic plants used as spices in the kitchen, but their secondary metabolites have also shown biological effects on human health. In traditional medicine, Piper species have been used worldwide to treat several diseases such as urological problems, skin, liver and stomach ailments, for wound healing, and as antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agents. In the present study, we attempted to isolate the phytochemicals from Piper caninum and Piper magnibaccum and evaluate their tyrosinase inhibitory activity.
MethodsPhytochemical constituents of the extracts were investigated using various chromatographic and spectroscopic methods. The structures of the isolated phytochemicals were established by analysis of their spectroscopic data, as compared to that of reported data. Tyrosinase inhibitory activity was also tested on the extracts and selected compounds using mushroom tyrosinase as the enzyme.
ResultsFractionation and purification of the extracts of Piper caninum and Piper magnibaccum afforded nine known compounds which were cepharanone A (1), cepharadione A (2), aristolactam AII (3), 5,7-dimethoxyflavone (4), 24-methylenecycloartan-3-one (5), βsitosterol (6), piperumbellactam A (7), 24S-ethylcholesta-5,22,25-trien-3β-ol (8) and stigmast-3,6-dione (9). Ethyl acetate extracts from leaves of P. magnibaccum gave the highest inhibition value at 48.35%, while the tested compounds displayed weak tyrosinase activity compared to the positive control, kojic acid.
ConclusionThese phytochemical results suggested that the extracts could assist as a potential source of bioactive compounds. Further research is needed in which the extract could possibly be exploited for pharmaceutical use.
Keywords: -Phytochemical, Piperaceae, Piper maingayi, Piper magnibaccum, Tyrosinase -
Pages 364-368Background
The current phytochemical study was carried out on a fraction of dried polar extract of aerial parts of Artemisia biennis Willd. which was previously reported to decrease the viability of the rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC12 in cell-based antioxidant assays.
MethodsA combination of solid phase extraction (SPE) and high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) of the hydroethanolic extract was used to purify the compounds. Structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic means, including 1H-NMR and MS analyses.
ResultsThree isolated and identified flavonoids in this study were luteolin, kaempferol and apigenin.
ConclusionThe cytotoxic potential of flavone aglycones, as the major components of selected fraction in the hydroethanolic extract of A. biennis might partly be related to the high death rate of PC12 cells.
Keywords: Artemisia biennis, Luteolin, kaempferol, Apigenin, PC12 cell line